What to Know About Using Time-Temperature Indicators for Cold Chain Supply Management
The purpose of cold chain management is to reduce and eliminate damage to products during movement from sourcing to end customer. It is especially relevant in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Successfully transporting cargo along the cold chain requires four fundamental components: cooling systems, cold storage, cold transport, and some type of distribution. In successful cold transport, creating and monitoring proper temperature is essential
. While creating a cold environment can be accomplished several ways—using gel packs, dry ice, and liquid nitrogen (among other things) for example—monitoring correct temperatures provides some challenges.

That’s where time-temperature indicators (TTI) enter the picture. A TTI can be an invaluable tool for preventing cold chain issues and enable successful cargo transport with few problems along the way. Here’s a short guide using time-temperature indicators at your business to handle all your cold chain needs.
What are time-temperature indicators?
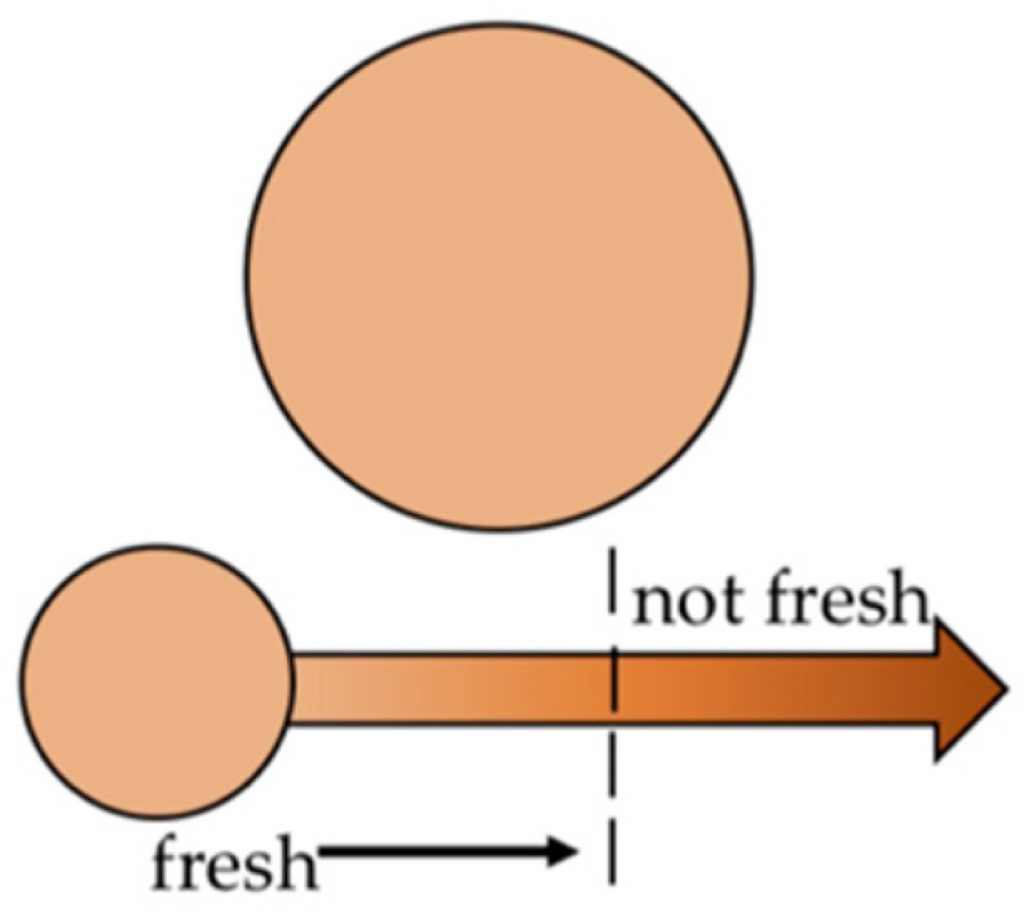
A time-temperature indicator (TTI) is a handy device that captures and displays the entire temperature history of a product. It’s a bit more advanced than a regular thermometer. Whereas a thermometer or temperature data-logger captures and measures the temperature, a TTI captures changes in temperature over a time period. For example, if a food product that must remain between 10 – 25 degrees somehow hits 30 degrees, a TTI can identify how long it was outside of the defined temperature range, so managers can determine if the product has been compromised or may be salvageable. This is even more useful today with the frailty and strict temperature requirements of the Covid-19 vaccine. Refrigeration equipment isn’t always 100% reliable, so TTI’s help companies determine if their products were damaged at any point during shipping. They’re perhaps most commonly used in food prep and service, but have broader cold chain management applications in medicines, pharmaceuticals, and other cold chain services.
How do they work?
TTI’s are remarkably straightforward. Some of them use dyes and filter paper to track temperature movement over time, while others may use pouches containing bacterial fluids that change color at certain temperature levels. With most standard TTI’s, a red dye runs through the display once it’s exposed to conditions beyond the indicator’s active temperature. If the temperature exceeds the TTI’s set threshold, the run-out of the dyes happens much faster, indicating longer exposure. In addition to serving the crucial purpose of monitoring product time and temperature, TTI’s are useful for remaining compliant with federal and industry cold chain regulations and are incredibly versatile for multiple shipments.
Advantages of using a TTI
Have you ever wondered about monitoring a product’s shelf life or whether the packaging is adequate as it travels? Do you need help making quick “accept or reject” decisions about products? Then you definitely need to use an effective time and temperature indicator for cold chain shipments. The benefits are simply amazing, not to mention comprehensive. To begin with, they’re an effective countermeasure for counterfeit items along a supply line, including food products and pharmaceuticals. TTI’s also aid with waste reduction and product damage while featuring tamper-proof designs intended to prevent anyone but suppliers, managers, and customers from messing with shipments. TTI’s are quickly and easily armed in the field. It doesn’t hurt matters any that they’re incredibly easy to read, use, and understand. With the right time-temperature indicators, it’s easier than ever to make fast, decisive decisions at the warehouse on whether to stop a shipment, re-route a product, or waste out and replace the product due to time-temperature abuse.
Temperature ranges
A high-quality Time Temperature Indicator should allow users to monitor a wide range of temperatures across a variety of traveling conditions. Fortunately, most TTI’s are versatile across an array of different cold chain management applications. These single-use devices feature a wide temperature sensitivity range, most often between 0°F/-18°C up to 99°F/37°C. Most temperature ranges will follow into the below categories:
- -18°C / 0°F
- 0°C / 32°F
- 2°C / 35°F
- 5°C / 41°F
- 8°C / 46°F
- 10°C / 50°F
- 20°C / 68°F
- 25°C / 77°F
- 30°C / 86°F
- 37°C / 99°F
Why such a broad range? Various products require different storage and transport protocols to remain safe. Some manufacturers also offer TTI’s in ranges specifically designed to keep vaccines (like vital COVID-19 vaccine) at a safe temperature while in transit. Each range uses a particular run-out time to mark the damage, so users know which products have been compromised or not. Taking full advantage of temperature ranges is the ideal way to ensure product safety at every step of your shipment route.
Real-world application
Whether most folks realize it or not, time-temperature indicators have a variety of real-world applications. Outside of shipping routes, almost every restaurant or foodservice business makes use of both thermometers and time-temperature indicators for safe food storage and transport. Product temperature checks occur through pharmaceutical supply chains to ensure vaccines and other life-saving medications aren’t compromised, spoiled, damaged, or rendered useless due to time-temperature abuse. At the end of the day, TTI’s are an invaluable cold chain management tool for monitoring temperature across the entire supply chain that will keep products safe, prevent damage or waste, and save everyone money in the long run.