What is a Lean Start Up?
Lean Startup is a set of business development processes used by entrepreneurs to develop products and markets in a fast and agile way.
Where did the concept come from?
The lean startup is a framework adopted from Toyota’s lean manufacturing model, which derived from the Toyota production system, this was a driving factor towards exponential growth throughout the 70’s. In the 90’s the TPS became lean. Lean is currently trending across the globe in the entrepreneurial space, driving startups to develop products with minimum input, maximum output, treating a startup as an experiment. The concept was applied to entrepreneurship by a visionary called Eric Ries. His book, ‘The Lean Startup’, discusses his concepts haven driven the methodology to the scale it is today, and how it works.
Are Lean Start Up methods only relevant to tech startups?
Lean framework’s can be applied outside of the tech industry. The concept lean promote’s, is about building towards a sustainable business model by providing a process to validate a demand for the product you want to build or the service you want to provide, before investing precious time and money into something you don’t yet know has a valid demand.
Lean allows a startup to adapt to the rapidly changing environment that has become of this interconnected world and increasingly social spaces. Sentimentality and entitlement have no place in the lean startup, passion for an overall vision is still as important as it has ever been to the entrepreneur, but why build a product, when you don’t really know if anyone wants it, and even less so when you don’t yet know, if users will pay for it?
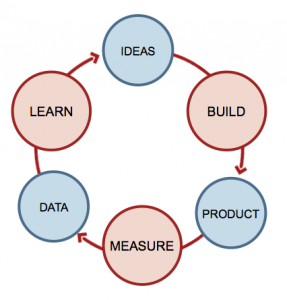
A lean startup has a vision, the way that this vision is delivered, is a variable, lean allows you to conduct carefully specific experiments, through certain stages of product development.
How do you begin to follow the process of Lean Startups?
Start by solving a problem for just one person, assume problem ‘x’, target customer ‘x’, assume the solution will be product ‘x’. Then define a set of assumptions that if incorrect, will completely invalidate your business model. Test the riskiest of these assumptions. If invalid, no demand for your specific solution, no early adopters desperate for your product or service to be released, pivot. Pivot by re-evaluating you customer, re-analysing your solution, and if required, redesign your problem. Then repeat.
This is the build – measure – learn cycle, this is what lean methodologies are built upon. If a business model is validated, begin again, this time with a minimum viable product, that meets the least amount of effort taken to produce the product you have found a gap in the market for, a demand for. Least amount of effort, maximum output. Then reiterate, build, measure and learn. Only add services and features that consumers validate through the experimental process your startup has become, eliminate the ones they don’t.
This concept can be adapted to almost every startup, not every element of the process will work for your business, but it is flexible. This is the core value of lean. There are various workshop’s across the globe lecturing on the lean startup, that can help put theory into practice, material online is growing everyday thanks to the success of the principles in practice across the world, and a great place to start is Eric’s book.
As a final note, I believe that lean is a way of thinking, it goes wholly against traditional business management and product development life cycles, but it promotes a, succeed fast, fail fast turn around, and this can only be useful in the rocky startup world, and a time of economic change. By minimizing waste and increasing productivity in consumer generated manner.
Related articles










